中藥綿萆薢於婦女更年期之應用
林志遠1、邱名榕1、王鯤淵2
1臺北長庚紀念醫院中藥科、2中國文化大學推廣教育部
摘要
正常女性的更年期平均年齡為51歲。更年期婦女嚴重、常見的症狀有燥熱(hot flushes)、盜汗(sweats)、肩膀痠痛(shoulder stiffness)、全身倦怠(general fatigue)。在更年期過渡期和停經後,許多婦女會經歷中度至重度燥熱(hot flushes)。Menopause hormonal therapy是目前治療燥熱(hot flushes)的治療方法,但是其副作用包括子宮內膜癌和乳腺癌的風險增加,限制了其臨床應用。一、停經後,女性的尿酸濃度升高至與成年男性相當。60-70歲女性的痛風發生率增加。在痛風臨床表現之前的平均無症狀高尿酸血症時間為10年或更長時間。二、停經後骨質疏鬆症已成為全世界的公共衛生問題。患有骨質疏鬆症的停經後婦女的骨質流失與雌激素(estrogen)缺乏或年齡有關。骨質疏鬆症的特徵是骨量低,微結構破壞和骨骼脆性增加,導致骨強度降低和骨折風險增加。三、薯蕷皂苷(dioscin)降低了人乳癌細胞MCF-7和MDA-MB-231的存活率。薯蕷皂苷是中藥綿萆薢(Dioscorea septemloba)的主要成分。薯蕷皂苷具有降尿酸,抗骨質疏鬆,抗腫瘤和抗動脈粥狀硬化的活性以及對肝纖維化的抑制作用。這些結果表明薯蕷皂苷是一種有生物活性的化合物,值得進一步研究。
關鍵字: menopause、hyperuricemia、osteoporosis、breast cancer、dioscin、Dioscorea spongiosa.
壹、前言
更年期婦女身體會因停經出現生理變化,一般2-5年,最短6個月,最長8-10年,平均1年,大部份(95%)在45歲到55歲之間更年期,平均停經(menopause)年齡為51歲1。黃帝內經.素問.上古天真論:「女子二七天癸至……七七天癸竭」,說明秦、漢時期(西元前221年-西元220年)觀察到女性14歲月經開始,49歲月經結束、更年期2。停經前期(pre-menopause)停經前的整個生育期。停經中期(peri-menopause)未完全停經前,月經型態開始改變,出現生理變化,月經停止未達一年。停經後期 (post-menopause)月經持續停止至少一年以上2。更年期婦女嚴重、常見的症狀有燥熱(hot flushes)、盜汗(sweats)、肩膀痠痛(shoulder stiffness)、全身倦怠(general fatigue)。Uptodate資料庫Martin et. al.不建議menopausal hormone therapy用於預防慢性疾病、心血管疾病、骨骼疾病1。 Menopausal hormone therapy禁忌症包括:乳癌、冠心病、靜脈血栓、中風、肝病1。中藥萆薢具有多種藥理作用,包括降尿酸、抗骨質疏鬆、抗腫瘤、抗真菌、降血脂、抗心肌缺血、預防動脈粥狀硬化。本文以天然物化學觀點,探討中藥萆薢療效的物質基礎,輔以現代研究說明化學與藥理,預期可有效改善生活品質。
貳、萆薢
萆薢之名始載於《神農本草經》,列為中品,約成書於秦、漢時期(西元前221年-西元220年)3。用於膏淋:萆薢味苦,其性下降,能利濕而分清去濁。為治小便混濁、或尿如米泔之膏淋要藥4。用於風濕痺症:萆薢能祛風溼、通絡止痛。可用於風濕痺症、腰膝酸痛、經脈屈伸不利4。中華本草:《植物名釋札記》解釋萆薢的藥名:以萆薢之療效,可知萆薢之義即痺解,謂其可以解除麻痺之病。凡草物名稱,其字從草,因而痺解即作萆薢了4。中華本草中藥萆薢收載粉萆薢和綿萆薢兩種4。
一、粉萆薢
中藥粉萆薢收載於2018年出版的臺灣中藥典第三版3。粉萆薢基原為薯蕷科(Dioscoreaceae)植物粉背薯蕷 Dioscorea hypoglauca Palib.之乾燥根莖3。主產湖南、浙江、江西、安徽等地。用途分類為祛濕藥(利水滲濕)。性味為苦,平。歸經歸腎、胃經。
二、綿萆薢
中藥綿萆薢收載於中華本草4。綿萆薢基原為薯蕷科植物(Dioscoreaceae)綿萆薢 Dioscorea spongiosa J. Q. Xi, M. Mizuno et W. L. Zhao或福州薯蕷 Dioscorea futschauensis Uline ex R. Kunth的乾燥根莖4。主產福建、江西、浙江。利濕去濁,祛風通痹。用於淋病白濁、白帶過多、濕熱瘡毒、腰膝痹痛。
三、薯蕷皂苷(dioscin)
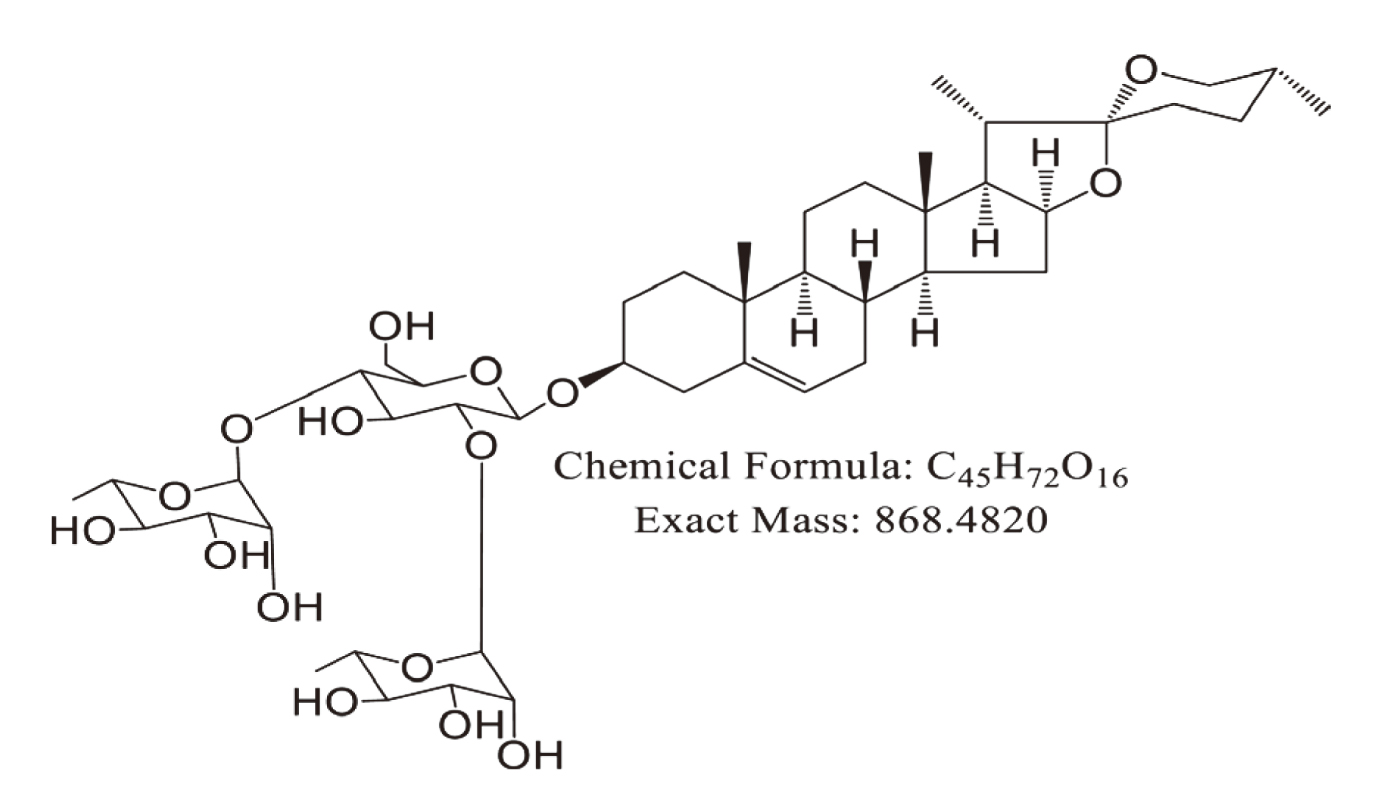
類固醇皂苷(steroidal saponin)大部份分布於百合科、薯蕷科(Dioscoreaceae)、石蒜科、玄參科、拔契科、豆科等植物中。薯蕷皂苷 diosgenyl 2,4-di-O-α-L-rhamnopyranosyl-β-D-glucopyranoside (dioscin)由薯蕷皂苷元(diosgenin)和三糖(chacotriose)組成5。(圖一)
圖一 薯蕷皂苷(dioscin)的結構5。
參、停經後高尿酸血症(postmenopausal hyperuricemia)
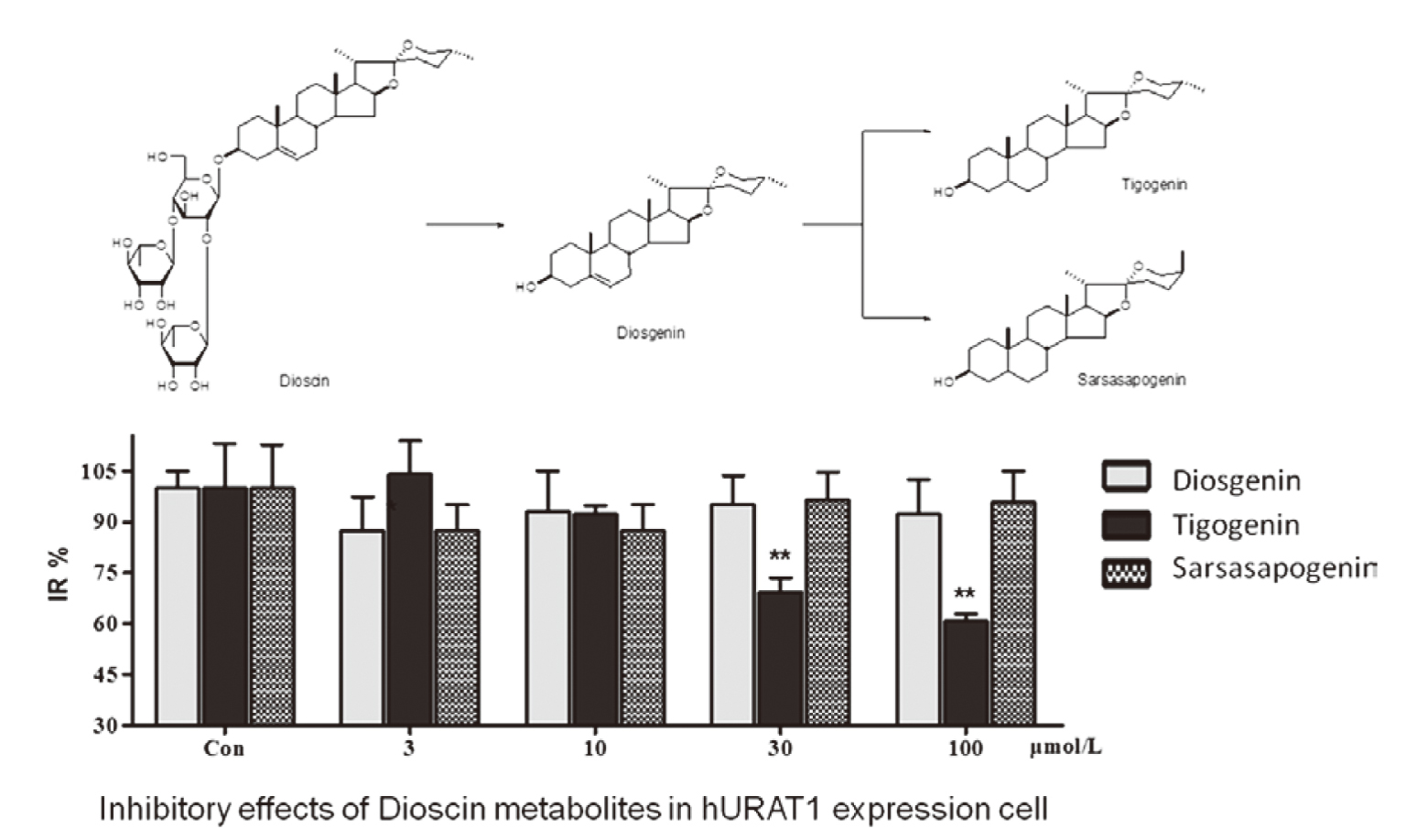
女性的血清尿酸濃度平均比相似年齡的男性低約1.0至1.5mg/dL,停經後,女性的尿酸濃度升高到與成年男性相當。在痛風臨床表現之前,平均無症狀性高尿酸血症時間至少為10年或更長時間。高尿酸血症是痛風的危險因子,60-70歲女性的痛風發生率增加6。降尿酸藥allopurinol降低血中尿酸的濃度,少數病人服用藥物後引發病人皮膚壞死,發生嚴重致命的藥物過敏反應。SJS (Stevens-Johnson Syndrome)病人皮膚壞死小於體表面積的10%,死亡率達10-25%。TEN (Toxic Epidermal Necrolysis)病人皮膚壞死大於體表面積的30%,死亡率將近40%7。2018年中國天津中醫藥大學Zhang et. al.研究dioscin的代謝產物tigogenin,是體內活性物質,降低血清尿酸濃度,增加尿酸排除8。儘管dioscin在高尿酸血症大鼠和小鼠中顯示出明顯的尿酸清除作用,但作為具有三糖的spirostanol steroidal saponin,在藥物代謝方面,dioscin難以吸收進入循環系統。口服薯蕷皂苷(dioscin)後,可以在血清和尿液中檢測到三種代謝產物:薯蕷皂苷元(diosgenin)、tigogenin、sarsasapogenin,沒有薯蕷皂苷(dioscin)原型(圖二) 8。從臨床藥理和藥物基因組學角度明確定義了URAT1對尿攝取的貢獻。尿酸主要通過腎臟排泄,其中90%通過尿酸轉運蛋白URAT1重新吸收回到血液中。利用表達人類URAT1的HEK293細胞係作為一種體外方法(in vitro)來研究dioscin代謝物通過hURAT1抑制14 C-尿酸攝取的能力。結果表明,與未轉染的模擬細胞相比,尿酸鹽的通透性顯著提高了30倍。在此篩選系統中,陽性對照RDEA3170的IC 50為40.0nM。Tigogenin表現出從10到100μM的顯著抑製作用,且呈濃度依賴性,而在100μM的濃度下,尿酸滲透率顯著降低至60%。Diosgenin和sarsasapogenin在抑制URAT1中對尿酸滲透性無統計學影響(圖二) 8。
圖二 薯蕷皂苷(dioscin)與代謝物:薯蕷皂苷元(diosgenin)、tigogenin,
sarsasapogenin的結構8。Inhibitory effects of Dioscin
metabolites in hURAT1 expression cell
Con:control group;IR:inhibitory rate compared
with control group(100%)
*p<0.05
**p<0.01 vs control group.
肆、停經後更年期骨質疏鬆症 (Postmenopausal osteoporosis)
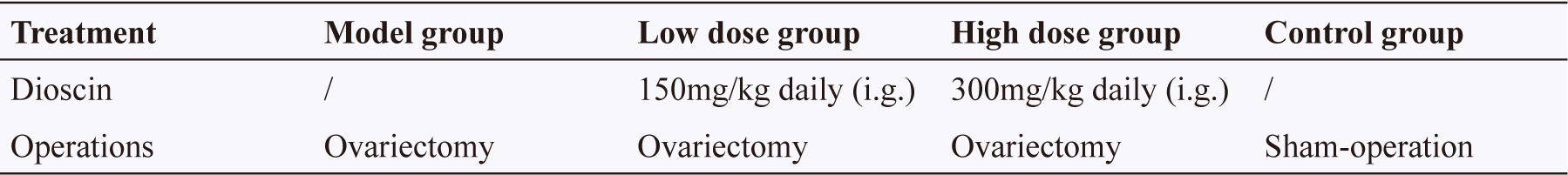
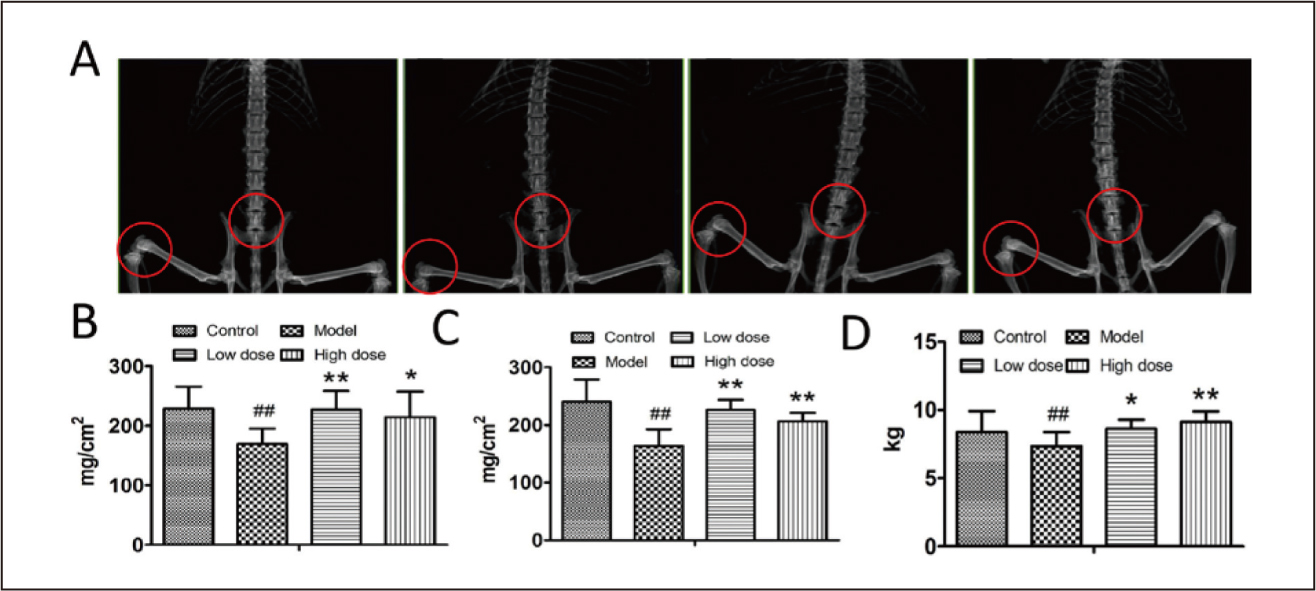
停經後骨質疏鬆症已成為全世界的公共衛生問題。Menopause hormonal therapy是目前停經後骨質疏鬆症的治療方法,但是其副作用(包括子宮內膜癌和乳癌的風險增加)限制了其臨床應用9。因此,迫切需要找到一種高效且副作用小的新藥。Dioscin是中藥萆薢的主要成分。2019年中國吉林大學第二醫院Wu et. al.檢查了dioscin對停經後骨質疏鬆症大鼠的作用並分析了其機理10。結果表明,用dioscin處理後,骨質疏鬆症大鼠的骨質密度和最終負荷增加。dioscin能促進骨質疏鬆症大鼠的骨小樑形成和骨分化。dioscin是骨質疏鬆症的潛在治療劑,值得進一步研究(表一、圖三)。
表一 The pharmacological treatment of rats10. intragastrically (i.g.)
圖三 Effects of dioscin on bone mineral density
(BMD), ultimate load and histopathological
evaluation in rats10. (A-C), Effects of dioscin
on the BMD of femur (A,B) and lumbar vertebra
(A,C), respectively. (D), Effects of dioscin on
the ultimate load of rat femurs. Results were
obtained from three independent experiments and
are expressed as mean ± SD.
#:p<0.05
##:p<0.01 vs. control group
*:p<0.05
**:p<0.01 vs. model group
骨質疏鬆可能是由於骨吸收過多引起的,調整骨吸收與形成之間的不平衡是治療骨質疏鬆的有效方法。2016年中國大連醫科大學Tao et. al.發現dioscin通過促進成骨細胞生成和抑制破骨細胞生成,可以顯著改善卵巢切除術誘導的動物模型的生化指標和微結構11。薯蕷皂苷(dioscin )可能是治療骨質疏鬆症的一種新穎而有效的候選藥物。
伍、in vitro cytotoxicity in MCF-7 and MDA-MB-231 human breast cancer cell lines with steroidal saponin dioscin
2016年美國Mississippi大學藥學院研究dioscin是否可以調節人乳癌細胞中的GATA3功能和細胞侵襲12。 Dioscin以濃度依賴性方式(concentration-depedent)和時間依賴性方式(time-depedent)降低了人乳癌細胞MCF-7和MDA-MB-231的存活率。Dioscin有潛力在乳癌中用作抗侵襲劑(表二)12。
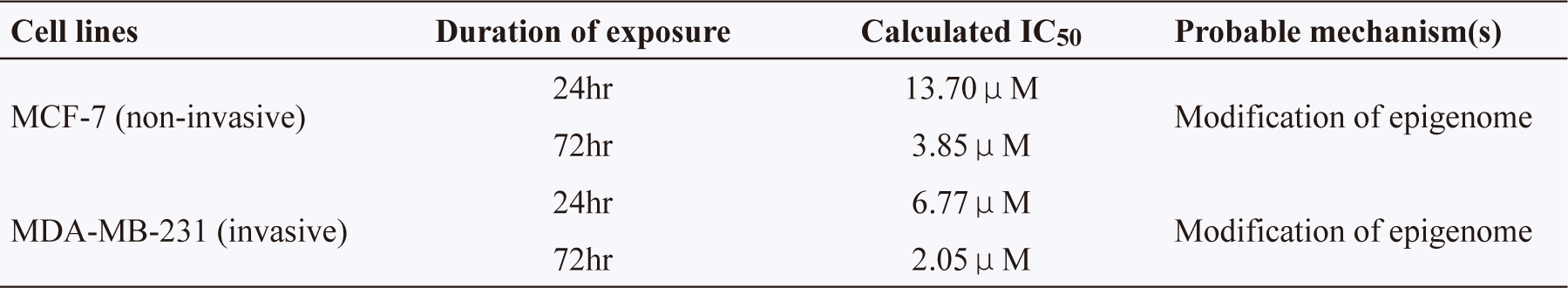
表二 IC50 of dioscin as determined in human breast cancer cell lines12
一、 Dioscin在培養條件或細胞環境中穩定
Dioscin的生物轉化(biotransform)可導致培養基或細胞環境中產生diosgenin。因此,評估了暴露72小時後培養基中以及細胞中dioscin的存在。在最高濃度的dioscin(5.76μM)下,在培養基或細胞裂解物中未檢測到diosgenin(dioscin的生物轉化產物)。dioscin在標準組織培養條件下穩定的結論。因此,測試dioscin對MCF-7或MDA-MB-231人體乳癌細胞的體外抗癌活性(in vitro cytotoxicity).
二、dioscin降低了MCF-7和MDA-MB-231人體乳癌細胞的增殖
通過用dioscin處理MCF-7和MDA-MB-231人體乳癌細胞24小時和72 小時,可以確定dioscin的抗細胞增殖活性。對於MCF-7人體乳癌細胞加藥後24小時IC50值為13.70μM,加藥後72小時後IC50值為3.85μM,對於MDA-MB-231人體乳癌細胞加藥後24小時IC50值為6.77μM,加藥後72小時後IC50值為2.05μM。綿萆薢所含的薯蕷皂苷(dioscin)能抑制腫瘤細胞人乳癌細胞MCF-7,IC50為3.85μM,腫瘤細胞人乳癌細胞MDA-MB-231,IC50為2.05μM。
陸、薯蕷皂苷(dioscin)的毒性
含薯蕷皂苷(dioscin)的DA-9801(Dioscorea japonica,D. nipponica標準化乙醇萃取物)於2015年在美國完成了治療糖尿病性神經病變的二期臨床試驗,表明其可接受的安全性5。此外,含dioscin的Di-Ao-Xin-Xue-Kang膠囊在中國已被用於治療心血管疾病(1994-2020年),並且自2012年以來已在荷蘭被批准用於治療5。在沒有引用任何其他毒性數據的情況下,臨床試驗的進入和進入藥品市場的批准足以證明dioscin用於治療用途的安全性。然而,2015年中國北京軍事醫學科學院Zhang et. al.研究大劑量的dioscin對人類肝細胞具有一定的毒性,推測臨床上長期服用含薯蕷皂苷(dioscin)類藥物,極有可能造成肝損傷13。久服中藥黃藥子(Dioscorea bulbifera L.)也會產生肝毒性,且黃藥子對肝組織損害的程度與劑量、給藥時間有關,這也可能與其所含成分薯蕷皂苷(dioscin)有關13。儘管dioscin濃度為μg/mL已在培養的細胞中顯示出肝毒性,但是薯蕷皂苷(dioscin)濃度為ng/mL表明對肝細胞保護作用5。但是,如果大劑量給藥,必須考慮薯蕷皂苷(dioscin)的毒性。在亞慢性毒理學評估中,大鼠的薯蕷皂苷(dioscin) LD50>300mg/kg/day5。
柒、Conclusion
中藥綿萆薢成分薯蕷皂苷(dioscin)不僅可以作為合成steroid hormone和口服避孕藥的原料,還可以作為抗高尿酸血症、抗骨質疏鬆、抗乳癌等藥物,改善更年期婦女停經後高尿酸血症、痛風、骨質疏鬆、乳癌。此外,已經合成了許多具有各種修飾的衍生物,從而極大地簡化了結構-活性關係的優化研究。Dioscin可能是開發針對多種疾病的療法中有希望的候選者。
Application of Dioscorea spongiosa in Healthy Menopause Women
Chih-Yuan Lin1, Alex Wang2 , Ming-Jung Chiu1
1Traditional Chinese Medicine Pharmacy, Taipei
Chang Gung Memorial Hosipital
2School of Continuing Education, Chinese Culture
University
Abstract
Normal women have menopause at a mean age of 51 years. Serious and common symptoms of menopausal women include hot flushes, sweats, shoulder stiffness, and general fatigue. During the menopause transition and postmenopause, many women experience moderate to severe hot flashes. Hormonal replacement therapy is the most popular treatment for hot flashes at present, but the side effects, including increased risk of endometrial cancer and breast cancer, limit its clinical use. After menopause, the urate concentrations in women rise to levels comparable to those in adult men. The increases in gout incidence are detectable in women by the sixth or seventh decades. An average period of asymptomatic hyperuricemia of at least 10 years or more in women prior to the clinical expression of gout. Postmenopausal osteoporosis has become a public health problem worldwide. Postmenopausal women with osteoporosis have bone loss related to estrogen deficiency or age. Osteoporosis is characterized by low bone mass, microarchitectural disruption, and skeletal fragility, resulting in decreased bone strength and an increased risk of fracture. Dioscin reduces the survival rate of human breast cancer cell lines MCF-7 and MDA-MB-231. Dioscin is the main ingredient of some medicinal plants such as Dioscorea hypoglauca and Dioscorea spongiosa. It is reported that dioscin has anti-hyperuricemia, anti-osteoporosis, anti-tumor and anti-atherosclerotic activity as well as an inhibitory effect on hepatic fibrosis. These results suggest dioscin may be a promising candidate for the development of treatments for various diseases.
參考資料:
1. Martin KA, Barbieri RL: Menopausal hormone therapy: Benefits and risks. UpToDate. Waltham, MA: UpToDate Inc. https://www.uptodate.com (Accessed on Feb 4, 2020.)
2. 酒小蕙,曹麗英,戎瑾如:更年期過渡概念分析。婦癌醫學期刊。2018;48:39-44.
3. 衛生福利部臺灣中藥典第三版編輯工作小組:臺灣中藥典第三版。2018. 台北市:衛生福利部。
4. 國家中醫藥管理局《中華本草》編委會:中華本草。1999.上海市:上海科學技術出版社。
5. Yang L, Ren S, Xu F, et al: Recent advances in the pharmacological activities of dioscin. Biomed Res Int. 2019;2019:5763602.
6. Gaffo AL: Clinical manifestations and diagnosis of gout. UpToDate. Waltham, MA: UpToDate Inc. https://www.uptodate.com (Accessed on Feb 4, 2020.)
7. 余光輝,黃獻立:實證醫學觀點看降尿酸藥物Allopurinol過敏基因HLA-B*5801檢測的臨床應用。台灣實證醫學學會會刊。2013;4(2):11-26.
8. Zhang Y, Jin L, Liu J, et al: Effect and mechanism of dioscin from Dioscorea spongiosa on uric acid excretion in animal model of hyperuricemia. J Ethnopharmacol 2018;214:29–36.
9. Rosen HN, Drezner MK: Overview of the management of osteoporosis in postmenopausal women. UpToDate. Waltham, MA: UpToDate Inc. https://www.uptodate.com (Accessed on Feb 4, 2020.)
10. Wu S, Zhao F, Zhao J, et al. Dioscin improves postmenopausal osteoporosis through inducing bone formation and inhibiting apoptosis in ovariectomized rats. Biosci Trends 2019;13(5):394-401.
11. Tao X, Qi Y, Xu L, et al: Dioscin reduces ovariectomy-induced bone loss by enhancing osteoblastogenesis and inhibiting osteoclastogenesis [published correction appears in Pharmacol Res. 2020 Jan;151:104397] Pharmacol Res 2016;108:90-101.
12. Aumsuwan P, Khan SI, Khan IA, et al: The anticancer potential of steroidal saponin, dioscin, isolated from wild yam (Dioscorea villosa) root extract in invasive human breast cancer cell line MDA-MB-231 in vitro. Arch Biochem Biophys. 2016;591:98–110.
13. Zhang YX, Wang YG, Ma ZC, et al: Preliminary study on hepatotoxicity induced by dioscin and its possible mechanism. Zhongguo Zhong Yao Za Zhi 2015 Jul;40(14):2748-52.
通訊作者:林志遠/通訊地址:台北市松山區敦化北路199號
服務單位:臺北長庚紀念醫院中藥科/聯絡電話:(O) 02-27135211 ext 3234